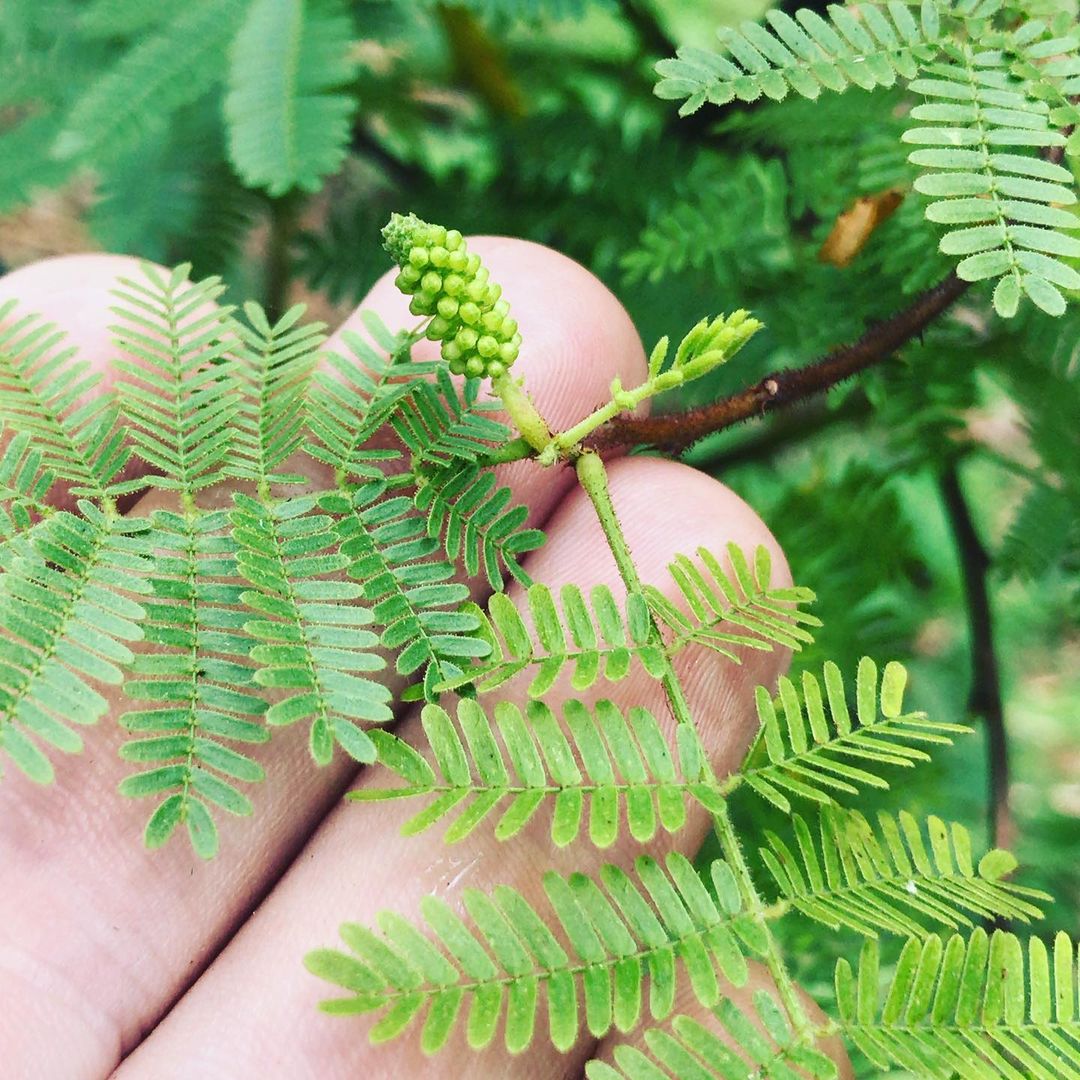
Mimosa Hostilis, scientifically known as Mimosa tenuiflora, is among the popular ethnobotanical trees with fern-like branches widely used for its healing properties since ancient times. Mimosa tenuiflora, as the natural psychedelic plant, has played an effective role in shamanism over the decades.
The evergreen tree has earned quite a reputation worldwide through its root bark that carries anti-inflammatory and cosmetic qualities.
Although the tree is tagged with various names such as Jurema and Columbia (traditional and local names), some people also refer to it as “tree of the skin” due to its amazing skin benefits.
Mimosa has been associated with the likes of Kratom due to its relative therapeutic and healing nature. Does the herb further compare with the popular Mitragyna Speciosa plant as we know it? Or does it show properties and characteristics completely different than that of Kratom? Read below to find out!
The Origin and Ecosystem
The perennial tree is indigenous to many South American countries, including Brazil, El Salvador, Panama, and Venezuela, up to Mexico’s northern and southern regions. Jungles situated in sub-tropical lowlands at altitudes of about 1000m provide an optimum and healthy ecosystem for Mimosa trees.
Mimosa trees are famous for their resilience and adaptability and can nurture in the severe conditions of tropical forests that hold long dry climates with spells of torrential rainfall.
As one of the pioneer plants, Jurema can grow in baren spots and also performs well in and after ecological disruptions. The shed leaves serve as mulch providing most of the necessary nutrients required for the plant’s survival.
Historical Value
Mimosa Hostilis has a centuries-old history of medicinal usage. The bark root of the tree was used by Mayan healers well before the 10th century as an effective remedy for treating skin lesions. Bark root boosts the skin regeneration process at a cellular level and reforms skin tissues. However, the use of the plant diminished in the 18th and 19th centuries.
The substance was reinstated as the subject of scientific studies and research in the 1080s after two calamities hit Mexico. A volcanic eruption that occurred in Chiapas, a southern part of Mexico, in 1982, and an explosion at a gas plant near Mexico City in 1984, caused many casualties and injuries of severe burns.
Because of the insufficient healthcare and medication, Red Cross deemed it safe to apply the root bark of Mimosa on the lesions and burns. The results proved fruitful. The wounded skin was reformed rather quickly. It was noticed that a new epidermal layer was formed on the surface in 26 days. After the 3-month cycle, the skin showed no signs of previous wounds.
With such surprising results, physicians started infusing grounded root bark into balms, soaps, and infusions as a remedy for curing skin infections and diseases.
Chemical Ingredients and Benefits
Mimosa Hostilis carries natural chemicals, alkaloids, and nutrients in abundant portions. Each component amounts to several healing benefits. Some main active chemical ingredients are;
- Arabinose – Also known as L-Arabinose, it protects the body against obesity and helps in reducing weight.
- Glucosides – have a high antioxidant ratio. Prevents the body from viral and bacterial infections. It prevents inflammation and is helpful for diabetic patients.
- Rhamnose – also referred to as a skincare chemical. It facilitates the production of collagen in the body, which helps in the regeneration of skin tissues.
- Saponins – protects the body against the acute levels of lead poisoning and keeps the cholesterol levels in the body in check.
- Lipids – regarded as an energy storage ingredient and also facilitate the body in performing routine functions.
- Phytosterols – is believed to diminish LDL cholesterol level in the body.
- Lupeol – considered an antioxidant chemical that protects against any kind of inflammation. Serves as an active component in treating malaria and arthritis.
- Tannins – popularly known as an anti-inflammatory chemical. It assists the body in the rejuvenation of epidermal tissues.
- Xylose – helps in increasing pancreatic activity.
- Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) – enlisted as a popular psychedelic that helps the body in recovering from trauma and prevents mental illnesses like PTSD.
Non-Medicinal Uses of Mimosa Tenuiflora
In addition to the surprising uses of Jurema in the medical field, the tree is also useful in a variety of non-pharmacological uses. Some of them are:
Animal Forage
Calumbi carries all essential nutrients and vital proteins required by animals thus can be an effective source of animal forage. Being an evergreen tree accustomed to harsh climates, it can be used as a year-long source of fodder for goats, sheep, and cows.
However, this type of forage is not recommended for pregnant livestock. Bees can also consume the forage in both dry and rainy seasons. The leaves and the bark of the tree can be used for washing animals as prevention against parasites
Fertilizer
Jurema, just like other plants, is considered to have nitrogen-fixing bacteria that help in soil fertilization. The perennial tree can fight off soil erosion and also helps in reforestation.
Natural Dye
Calumbi is also valued as a dyeing substance considering its high tannin content. The tree has reddish-brown wood with a yellow core. The epidermal layer is greyish brown with vertical splits. These natural pigments give off brown to purplish shades and are popularly used as a textile dye to provide vibrant yet long-lasting results.
Natural Cosmetic
Jurema is rich in chemical ingredients like tannin and rhamnose, which promote skin healing., making it an all-natural skincare. Both of these compounds initiate and strengthen collagen production in the body, promote tissue formation, and help skin rejuvenation at a cellular level.
Apart from treating burns and lesions, they also help in the removal of scars on the body. This is why it is commonly used as a supplementary substance used in a wide range of cosmetics and beauty products, including; shampoos, beauty soaps, lotions, and creams.
Mimosa root bark harbors antifungal and antimicrobial functionalities. Cosmetic products containing root bark powder help against acne, eczema, wrinkles, stretch marks, spots, and other skin infections. When used in shampoos, it prevents dandruff and allows hair to become long and thick.
Cultivation
If you have been associated with kratom in any way, you would know that cultivating and producing kratom on US soil is completely prohibited. Which might make you wonder if the laws for cultivating Jurema are the same or not.
For starters, planting Mimosa Tenuiflora is permitted as of now but selecting the right type of soil might prove troublesome. The preferable environment for Mimosa cultivation is alongside the northern parts of South America.
Their resilience to grow in the most extreme ecosystems enable them to bloom in most parts of the world. Still, it is important to keep note of the plant hardiness zone map in case you are planting outside. Under normal circumstances, USDA Zone 9 is recommended.
Seeds are released after pods are exposed to the sun. Once the seeds are released, they can be planted on sandy soil. Mechanical scarification of the seeds is carried out to boost the germination process of the seeds. The favorable temperature for seed germination is 20 – 30°C although the germination process accelerates at about 25°C.
Scientific Researches
Tepezcohuite wasn’t the subject of discussion for scientists up until the end of the 19th century. The tree was subjected to experimentation only after they showed astonishing healing effects in the 1890s tragedies. After which, root bark started being used as a necessary component in soaps and other by-products.
Scientific research published in 2006 investigates the use of mimosa Tenuiflora extract in the treatment of leg ulcers. The study conducted in a controlled environment found out that the wound shrunk up to 90% in the entire group of test subjects, without any signs of side effects.
Another study was conducted in 2011, which tested the therapeutic effectiveness of an extract taken from Mimosa Tenuiflora for leg ulceration treatment. The study showed similar results. Almost 12 different studies have been conducted on a similar matter.
Many biological investigations have studied the psychoactive components and chemical compounds present in the bark. The studies reflected high amounts of saponin and tannin contents. Tannin was observed to be the primary component that protected the wound against bacterial infection.
Legal Status of Mimosa Hostilis Root Bark
The legality status of every organic substance that is newly introduced to the market comes into question in the US, mostly when they carry psychoactive or healing properties. Unlike kratom that has faced countless legality issues worldwide and especially in America, Mimosa Hostilis is entirely legal at the moment despite being subjected to various uncertainties.
The legality status of the tree can be overturned owing to one of its active ingredients. Dimethyltryptamine, also called DMT, is considered a highly potent and effective psychedelic. The root bark solely contains about 1% to 17% of DMT.
Despite the trees’ lack of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MOAIs) that diminish the psychedelic effects of the root bark, many users have reported experiencing such effects regardless, which pose a threat to its legal status but up to a certain level. Imposing a ban or even regulating the use of Jurema can be tricky for US drug regulatory authorities due to the United Nation’s convention.
According to article 32 of the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances, the traditional usage of certain organic substances carrying medicinal uses should not be prohibited. Plants carrying psychotropic substances can be legalized for use by determined groups for religious purposes should not be subject to a ban. This employs the legitimacy of the root bark in most countries worldwide.
The alkaloids and other psychoactive components present in kratom are labeled as schedule 1 drugs and do not meet the article 32 criterion to pass out as a legitimate drug. Thus the legality of ketum is in question internationally.
Mimosa Hostilis and Kratom – Comparison
Tepezcohuite is deemed related to Kratom in a lot of aspects. From their physical aspects to their chemical composition, both substances have a lot in common.
Ethnobotanical Substances
Both of the organic plants have a rich history of cultivation and consumption. Being native to Southeast Asia, Kratom poses a threat and has had a healthy relationship with the natives for hundreds of years.
Kratom has been used due to its energy-boosting and tranquilizing properties over the years and has proved beneficial results.
Mimosa Hostilis adopted quite a similar approach. Its surprising healing properties were no secret to the Mayan healers who have used it for centuries.
The root bark powder is rapidly gaining popularity in the global communities and is finding its way to international markets just like kratom.
They can be ingested in several distinct ways. Both can be taken as raw or can be brewed into coffee or tea or added to standard drinks.
Healing properties
Kratom offers therapeutic and healing properties eradicating a wide range of physical and mental disorders in users similar to that of Jurema.
The plants have been ingested by the natives in their true form since ancient days.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory components are common among both substances.
Can You Mix Kratom and Mimosa Hostilis Together?
Mixing the two powders in search of an enhanced effect isn’t encouraged as the MAOIs and kratom make an unhealthy combination. However, due to less research available, it is better to not experiment with anything on your own without expert consultation.
If you do not like the taste of kratom, there are other simpler combinations to help you out with the problem. For example, mixing kratom with orange juice or coffee may be a great way to enhance the potency and flavor of the herb.
Final Thoughts
Mimosa Hostilis carries phenomenal healing and therapeutic properties on par with any other organic material. However, despite having multiple health benefits it is highly necessary to be cautious while ingesting the root bark powder.
Despite being legal in most states around the world, the tree carries psychedelic and hallucinogenic characteristics that might pose a threat to your health. Make sure you consult your doctor if you feel any kind of adverse symptoms. You should also be careful of the product’s quality as there are many vendors selling low-quality and even fake Columbia.
Nevertheless, Jurema is a highly beneficial organic powder that can be used for a wide range of purposes apart from human use. If Jurema is not to your taste, you can always feed them to your livestock as forage. But, If you want to stick with the lab-tested and high-quality kratom powder we can be your number one choice.